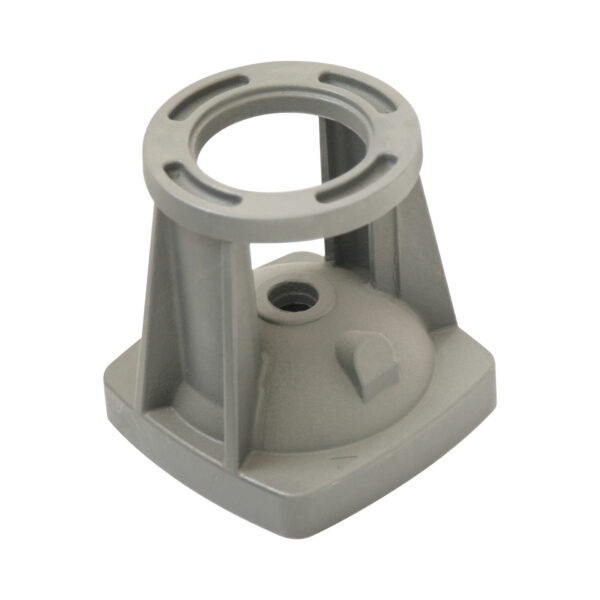
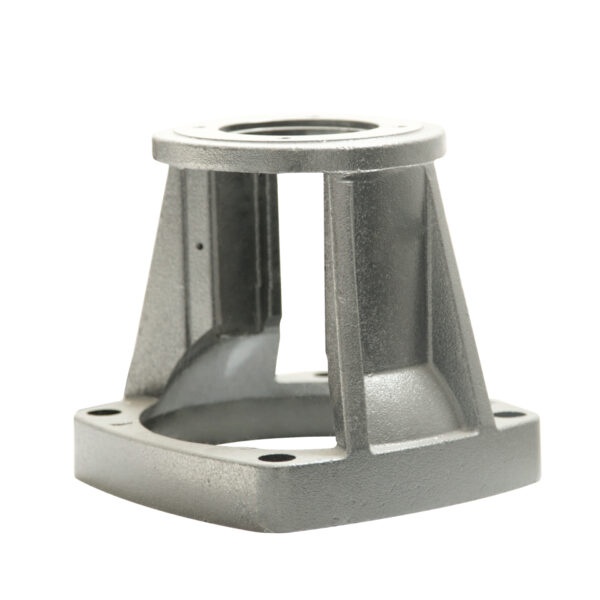
Agricultural machinery Components
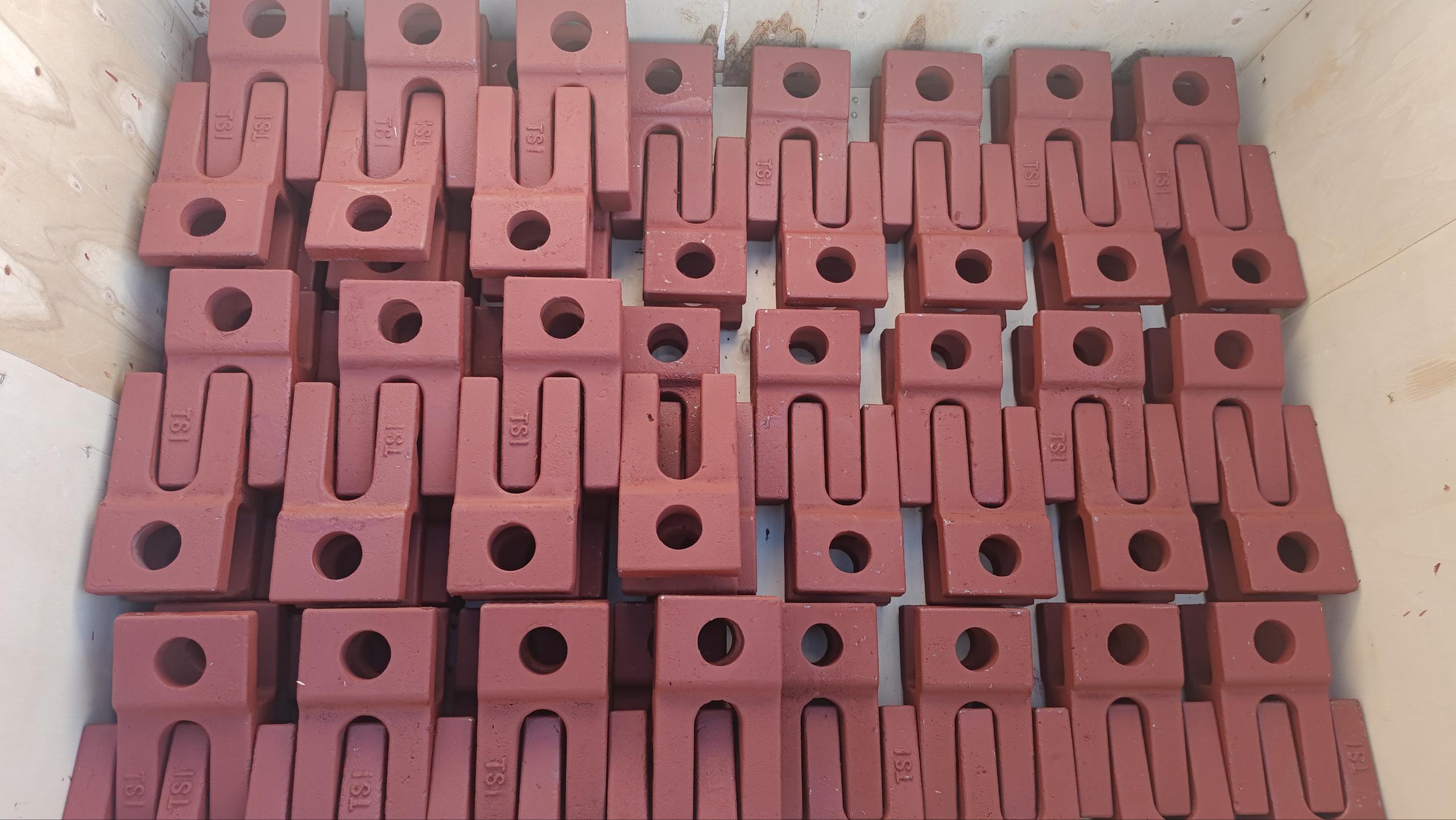
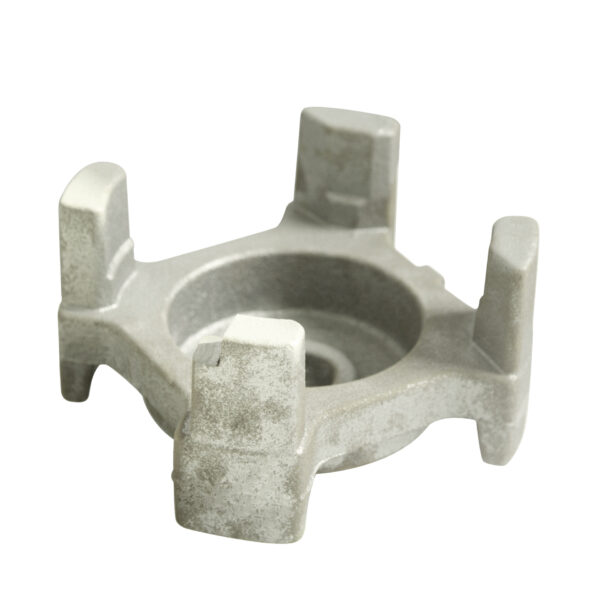
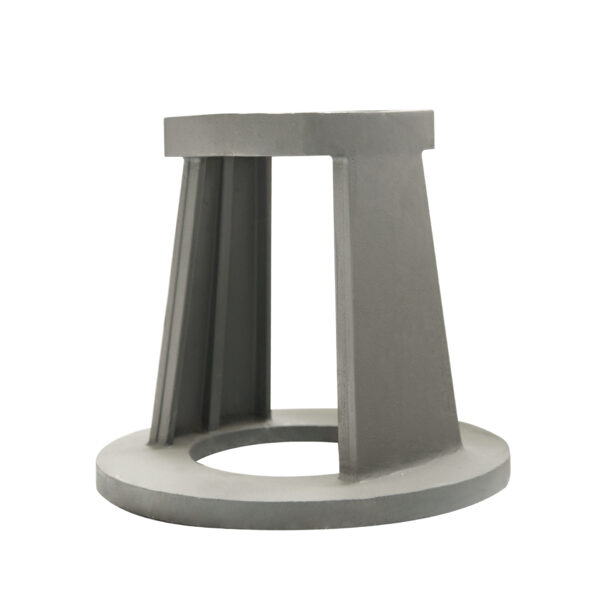
Grey iron castings are widely used in agricultural machinery due to their excellent vibration damping, dimensional stability, and cost-effectiveness. Typical parts include gearbox housings, counterweights, bearing housings, pump bodies, brackets, and structural bases. Grey cast iron offers ideal performance for agricultural equipment that operates under medium loads and requires high reliability in dusty, high-vibration environments.
Key Features
High vibration damping capacity
Reduces stress and prolongs the life of mechanical assemblies operating in rough field conditions.
Stable dimensions and shape retention
Prevents warping or misalignment under thermal cycling and dynamic loading.
Good thermal conductivity
Helps dissipate heat from moving or rotating components during prolonged operation.
Excellent machinability
Allows for precise secondary processing such as drilling, tapping, and surface finishing.
Cost-effective solution
Compared to ductile iron or steel, grey iron provides a durable yet economical option for mass production of agricultural parts.
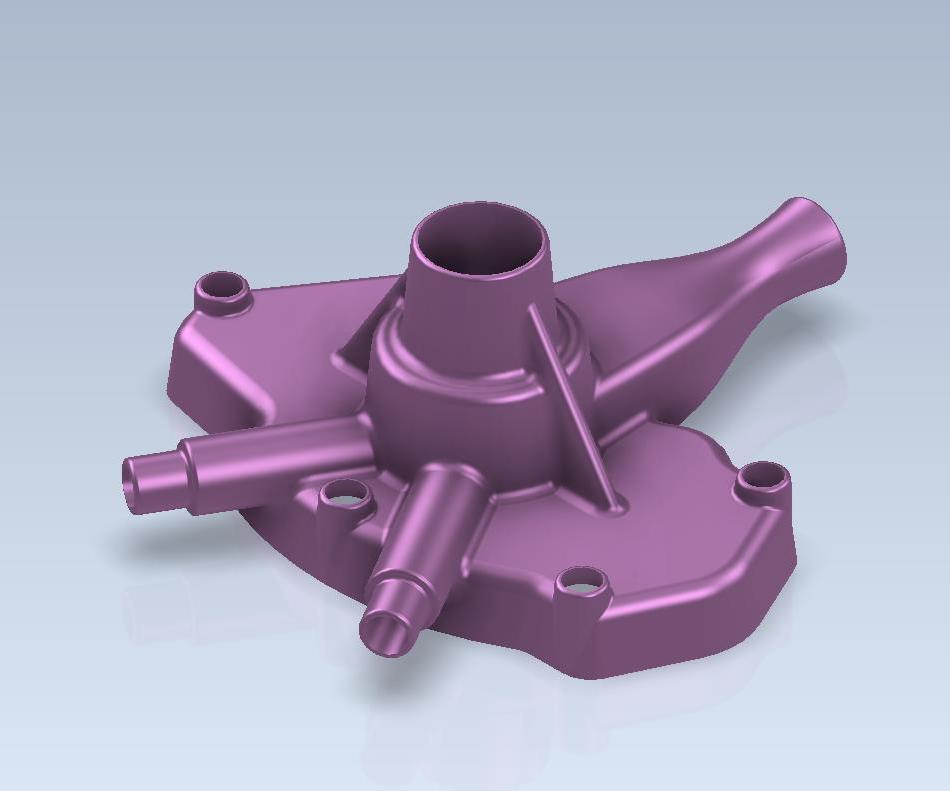

3D models are created based on customer drawings, considering shrinkage and machining allowance.
Patterns are CNC-machined from wood, aluminum, or resin, depending on accuracy and production volume. Wood is used for small batches, aluminum for durability, and resin for complex, high-precision parts.
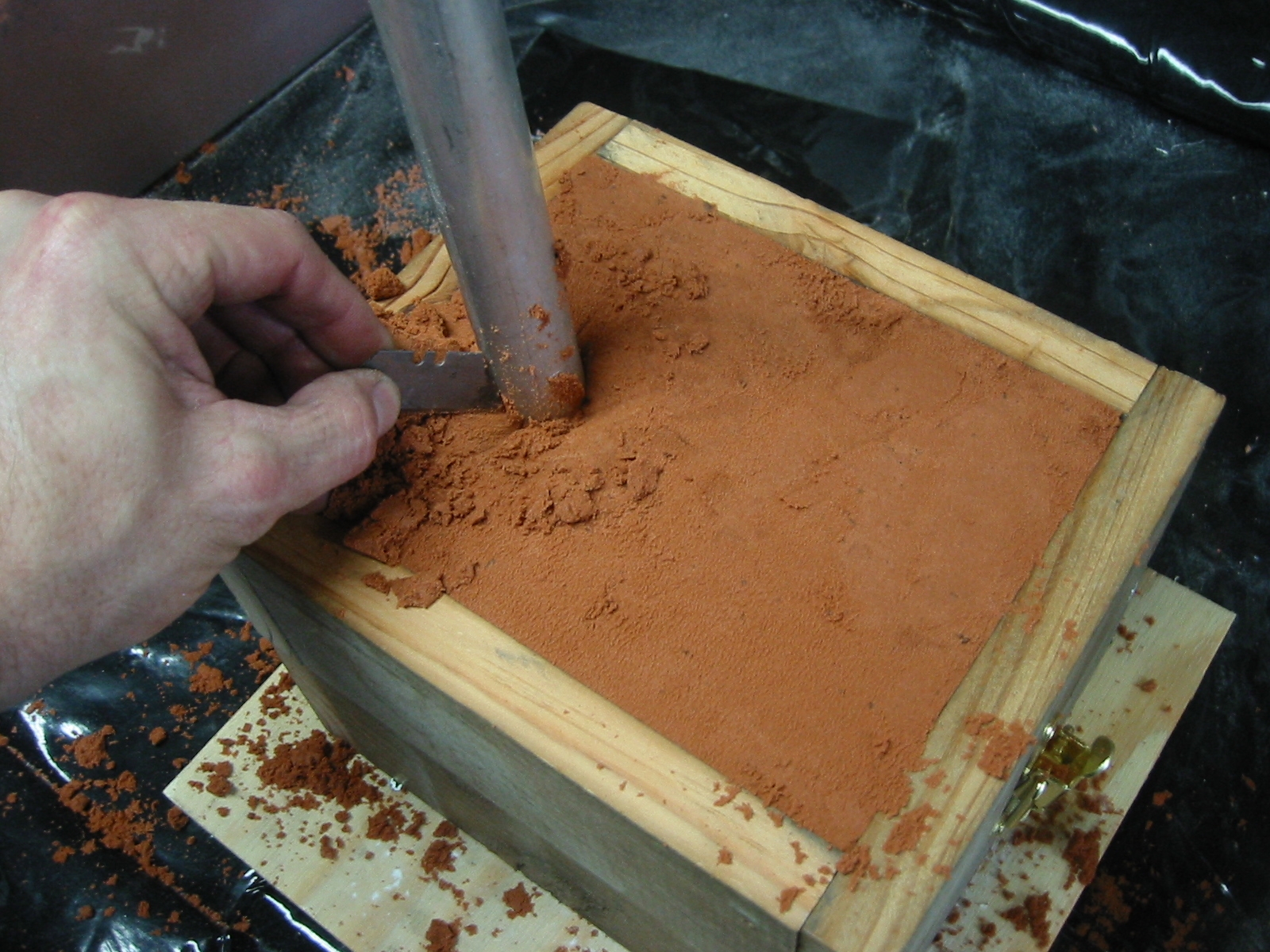

Green sand molding is used for standard shapes and high-volume production, offering good economy and speed. Resin sand molding is selected for complex geometries or tighter tolerance needs.
Cores are made when internal passages are required. Core shooting machines produce sand cores using cold-box or hot-box technology, which are then precisely placed into the mold before pouring.
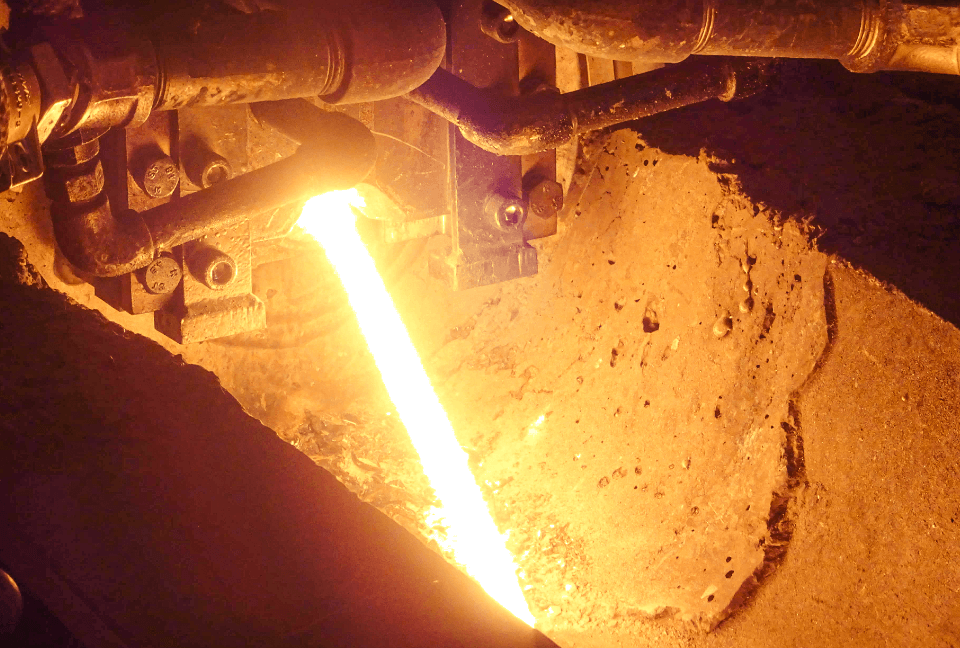
Grey iron is melted in a medium-frequency induction furnace. The raw material mix typically includes pig iron, scrap steel, and recycled castings to ensure stable composition.
Molten iron is poured into the prepared molds at controlled temperatures, usually between 1350°C and 1450°C, to ensure smooth flow, complete filling, and minimal casting defects.
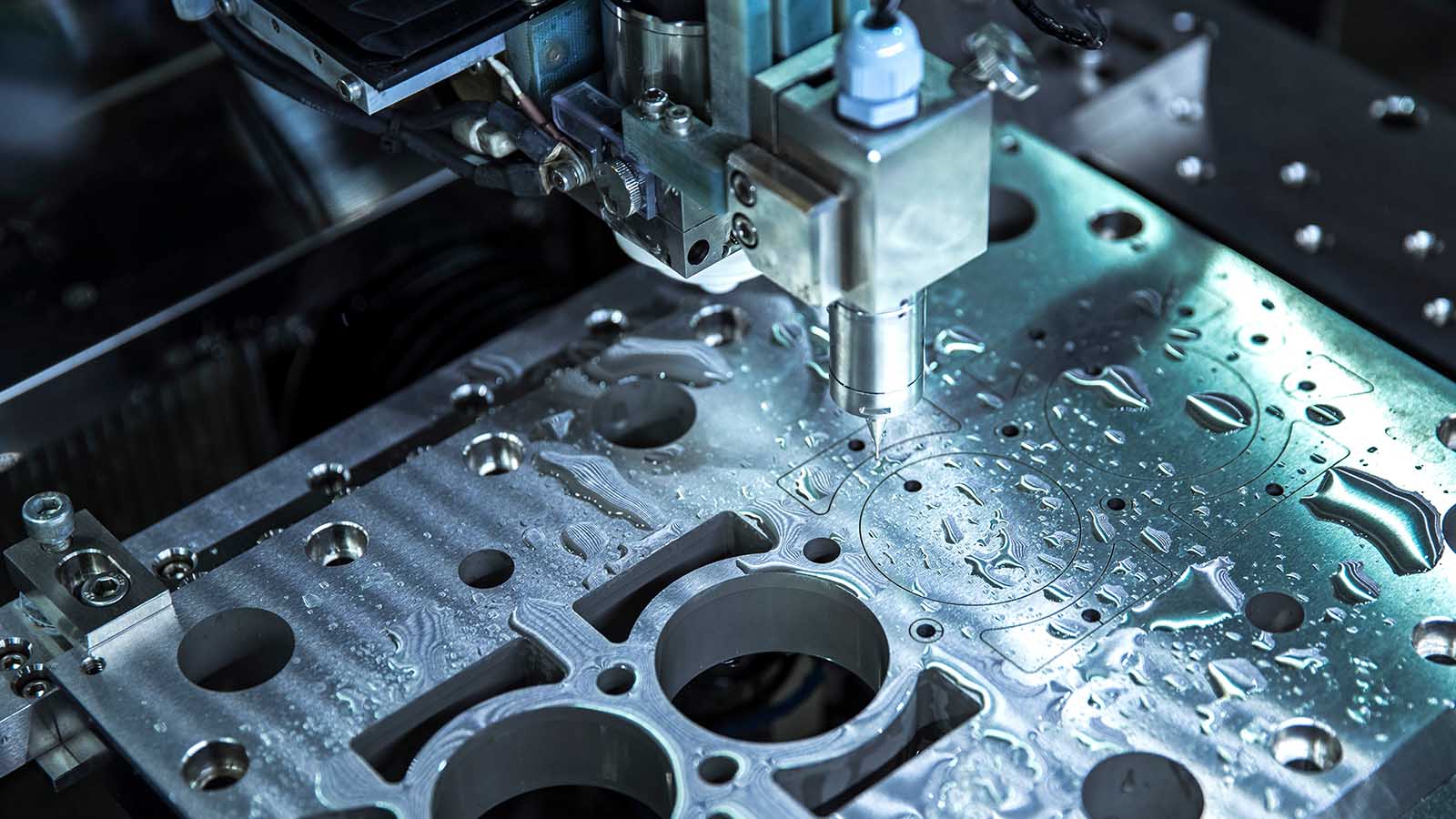

CNC machining is applied to critical surfaces to achieve required tolerances and finishes. This includes milling, turning, and surface grinding as needed.
Holes are drilled and threads are tapped according to drawing specifications. Additional treatments such as deburring or surface coating may also be performed upon request.

Castings are cleaned by shot blasting to remove sand residue, scale, and oxides, revealing the metal surface underneath.
Fettling involves removing gating systems, risers, and any excess material using cutting tools or grinders. Care is taken not to affect dimensional accuracy.

Castings are cooled in the mold under controlled conditions to minimize internal stress and distortion. Cooling time varies depending on part size and wall thickness.
After cooling, molds are broken apart and the castings are removed. The sand is separated and recycled for use in future molds.

3D models are created based on customer drawings, considering shrinkage and machining allowance.
Patterns are CNC-machined from wood, aluminum, or resin, depending on accuracy and production volume. Wood is used for small batches, aluminum for durability, and resin for complex, high-precision parts.

Green sand molding is used for standard shapes and high-volume production, offering good economy and speed. Resin sand molding is selected for complex geometries or tighter tolerance needs.
Cores are made when internal passages are required. Core shooting machines produce sand cores using cold-box or hot-box technology, which are then precisely placed into the mold before pouring.

Grey iron is melted in a medium-frequency induction furnace. The raw material mix typically includes pig iron, scrap steel, and recycled castings to ensure stable composition.
Molten iron is poured into the prepared molds at controlled temperatures, usually between 1350°C and 1450°C, to ensure smooth flow, complete filling, and minimal casting defects.

CNC machining is applied to critical surfaces to achieve required tolerances and finishes. This includes milling, turning, and surface grinding as needed.
Holes are drilled and threads are tapped according to drawing specifications. Additional treatments such as deburring or surface coating may also be performed upon request.

Castings are cleaned by shot blasting to remove sand residue, scale, and oxides, revealing the metal surface underneath.
Fettling involves removing gating systems, risers, and any excess material using cutting tools or grinders. Care is taken not to affect dimensional accuracy.

Castings are cooled in the mold under controlled conditions to minimize internal stress and distortion. Cooling time varies depending on part size and wall thickness.
After cooling, molds are broken apart and the castings are removed. The sand is separated and recycled for use in future molds.
Quality Inspection
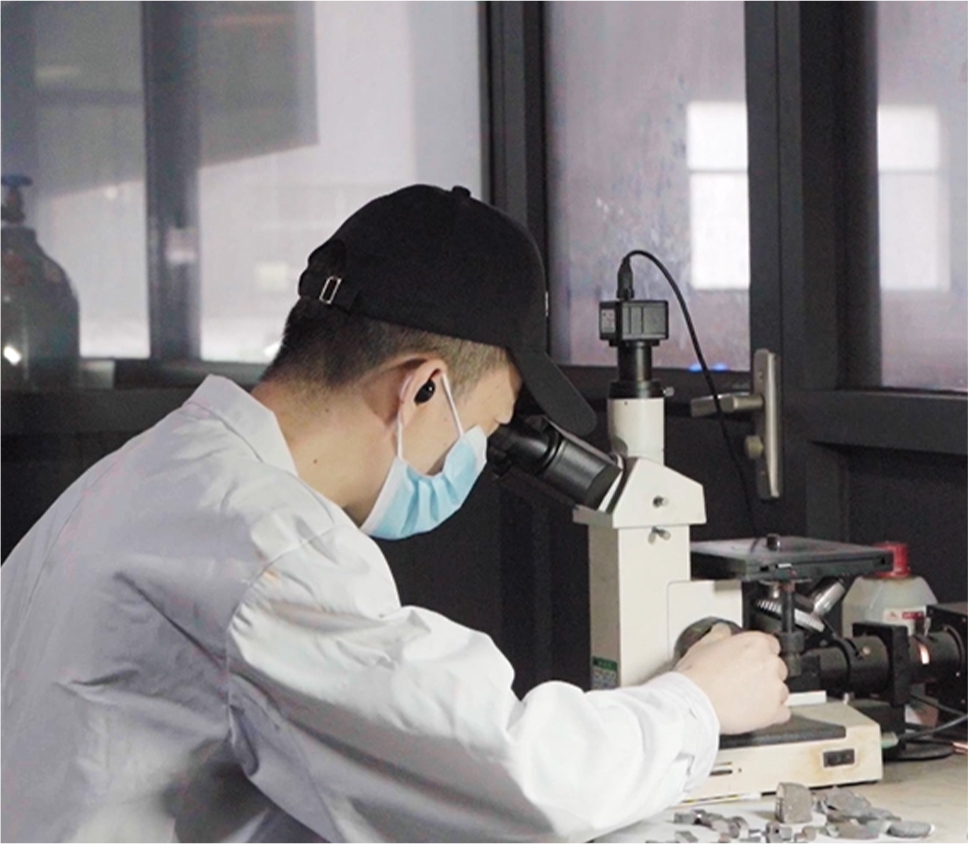
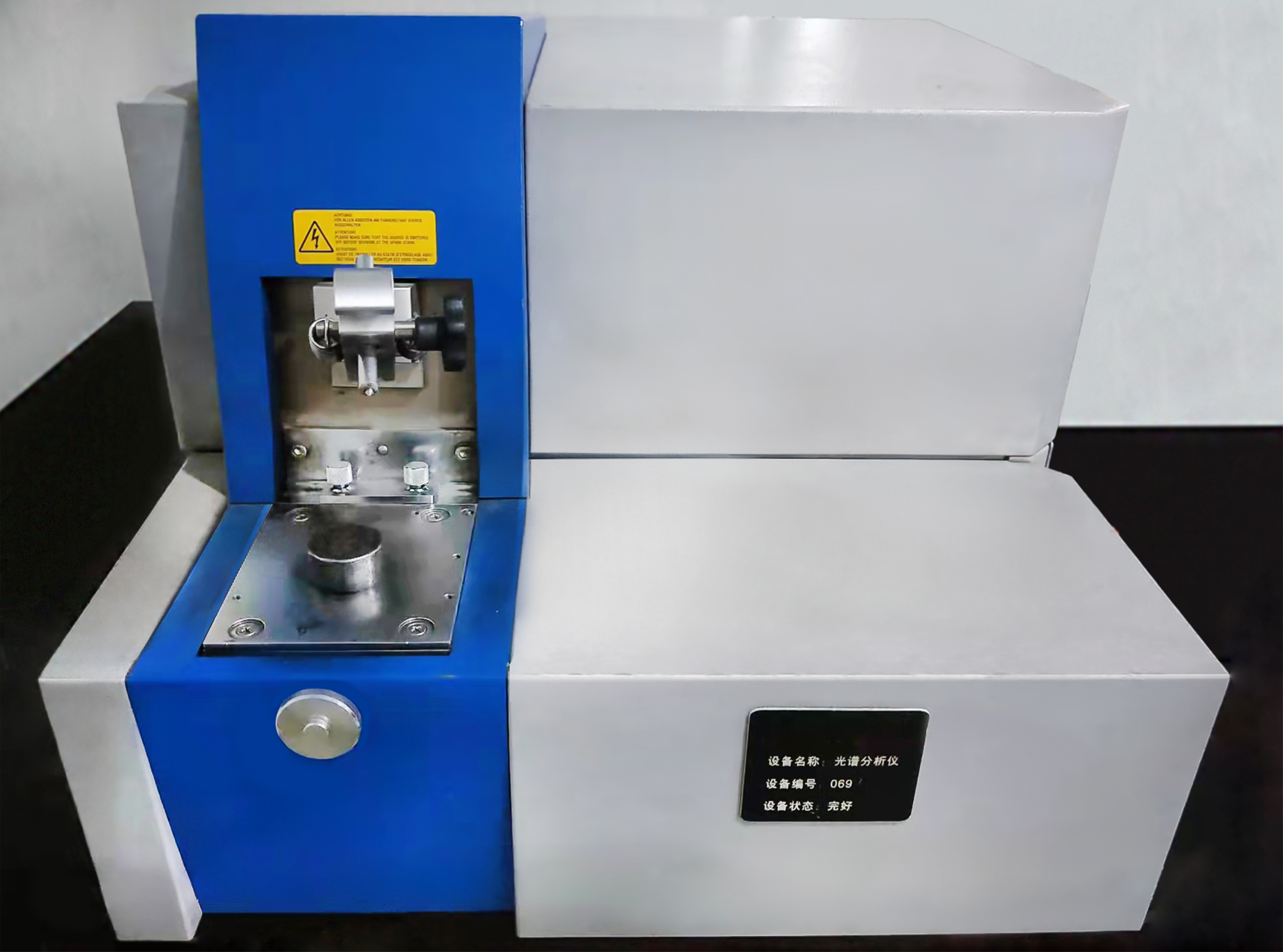
Chemical Composition Testing
Each heat is spectrometer-tested to ensure compliance with required material grades (e.g., EN-GJL-250, ASTM Class 40).
Mechanical Property Testing
Tensile strength and hardness are verified using standard test samples to ensure consistent mechanical performance.
Dimensional Inspection
Critical dimensions (hole spacing, mounting faces, overall geometry) are measured using calipers, gauges, or CMM equipment.
Surface Defect Inspection
Visual checks and magnetic particle inspection are used (if required) to detect cracks, shrinkage, or surface flaws.



Rust Protection Treatment
Before packaging, all castings undergo anti-rust treatment to ensure corrosion resistance during transportation and storage. Common treatments include applying anti-corrosion oil or a water-based rust inhibitor, especially for machined surfaces and critical contact areas.
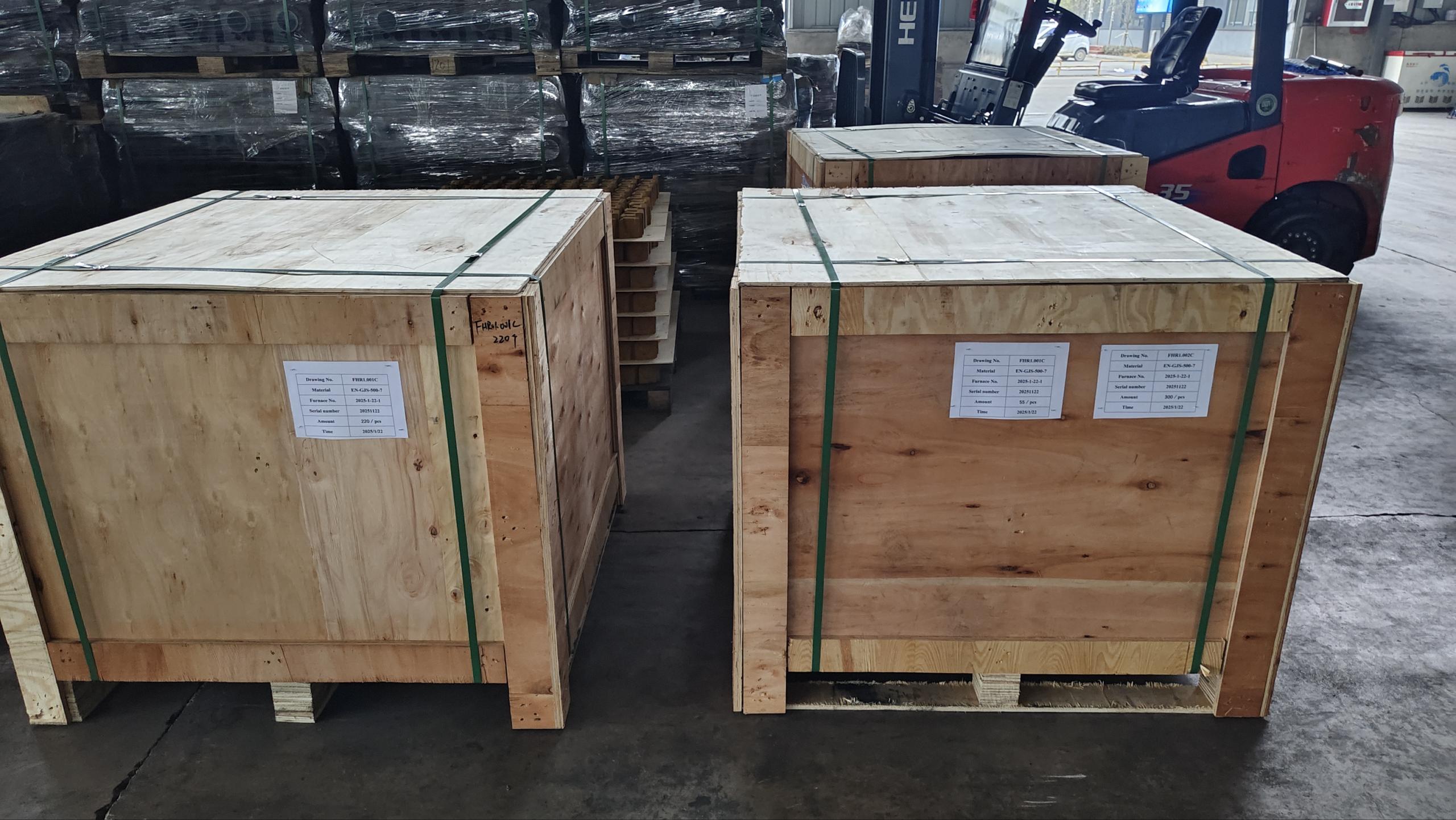
Secure and Export-Ready Packaging
Each product is carefully packed in fumigation-free wooden crates or reinforced wooden pallets to ensure safety during handling and long-distance shipping. The packaging is compliant with international export standards (ISPM-15) and suitable for sea, air, or land transport.
-
Heavy or large parts are secured with steel straps and foam pads to prevent shifting or collision.
-
Small and medium-sized castings are individually wrapped and separated with protective padding to avoid surface damage.
-
If required, desiccant or shrink film is added inside the packaging to control moisture.
Customized Labeling and Marking
We provide customized labels, barcodes, and product markings based on customer requirements. Typical markings include:
-
Part number and revision code
-
Purchase order number
-
Heat number or batch number for full traceability
-
Customer logo or destination tags (if needed)
Lead Time
Standard lead time is 45 to 55 working days, depending on:
-
Order quantity
-
Whether machining or special testing is required
-
Pattern availability and casting complexity
Urgent delivery requests or phased shipments can be arranged upon agreement.















